Let explore Angular Date Pipe, by learning how to use and will demonstrate an example of its use cases. Angular’s built-in DatePipe is a powerful tool for formatting date values in your application’s templates. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how to use the DatePipe effectively in the latest version of Angular, covering both basic and advanced usage.
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to use Angular’s DatePipe to format dates in different formats within a component template.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Angular’s DatePipe
The DatePipe transforms a date value into a desired string format. It can handle various input types, including JavaScript Date objects, numbers (milliseconds since UTC epoch), and ISO 8601 strings
2. Basic Angular DatePipe Syntax
The basic syntax for using DatePipe in Angular templates is:
{{ dateValue | date[:format[:timezone[:locale]]] }}The Date input can be provided as a date object, milliseconds, or an ISO date string, and we can convert this to our desired date format using an Angular date pipe. The Angular Date Pipe offers various date formats, including predefined and custom date formats. The syntax for the date pipe is as follows:
Where:
dateValueis the date to be formattedformatis an optional string that defines the output formattimezoneis an optional timezone offsetlocaleis an optional locale code for localization
3. Angular Date Pipe Examples in Angular 18
To better understand how Angular date pipe works, we demonstrate an example with and without date pipe.
Where now is the current date and time, we can see that without the date pipe we are displaying all information about the date and time. Let’s define now in our typescript and add a date pipe example in the component template.
We need to import DatePipe from the angular common module to work with date.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { DatePipe } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<h2>Angular DatePipe Examples</h2>
<p>Current Date (default): {{ today | date }}</p>
<p>Custom Format: {{ today | date : 'dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss' }}</p>
<p>Predefined Format (full): {{ today | date : 'full' }}</p>
<p>
Localized Date (French): {{ today | date : 'long' : 'GMT+1' : 'fr-FR' }}
</p>
`,
standalone: true,
imports: [DatePipe],
})
export class AppComponent {
today: Date = new Date();
}4. Predefined Date Formats
Angular provides several predefined date formats for convenience:
'short': equivalent to'M/d/yy, h:mm a'(e.g., 6/15/15, 9:03 AM)'medium': equivalent to'MMM d, y, h:mm:ss a'(e.g., Jun 15, 2015, 9:03:01 AM)'long': equivalent to'MMMM d, y, h:mm:ss a z'(e.g., June 15, 2015 at 9:03:01 AM GMT+1)'full': equivalent to'EEEE, MMMM d, y, h:mm:ss a zzzz'(e.g., Monday, June 15, 2015 at 9:03:01 AM GMT+01:00)
The Date pipe accepts three arguments format, timezone & locale. We don’t need to use them all, the date format is used frequently, and others are optional and used when we really need them.
| Argument | Description |
| format | For the desired output format of date, we can use either a predefined date format or a custom date format using symbols. |
| timezone | Optional. Default is undefined. A timezone offset (such as ‘+0430’), or a standard UTC/GMT or continental US timezone abbreviation. |
| locale | Optional. Default is undefined. A locale code for the locale format rules to use. |
4. Custom Date Formats in Angular Date pipe
For more control, you can create custom date formats using these symbols:
y: YearM: Monthd: Day of the monthE: Day of the weekh: Hour (1-12)H: Hour (0-23)m: Minutes: Secondz: Time zone
Example of a custom format:
<p>{{ today | date:'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss Z' }}</p>
We have implemented the above example in our code in the app.component.ts file.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { DatePipe } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<section>
<p>
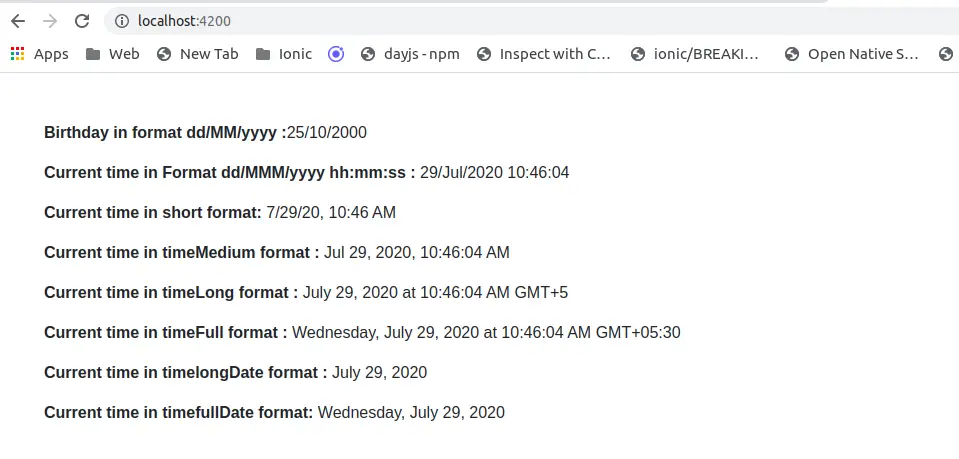
<b>Birthday in format dd/MM/yyyy :</b>
{{ birthday | date : 'dd/MM/yyyy' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in Format dd/MMM/yyyy hh:mm:ss : </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'dd/MMM/yyyy hh:mm:ss' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in short format: </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'short' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in timeMedium format :</b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'medium' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in timeLong format : </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'long' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in timeFull format : </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'full' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in timelongDate format : </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'longDate' }}
</p>
<p>
<b>Current time in timefullDate format: </b>
{{ nowDateObject | date : 'fullDate' }}
</p>
</section>
`,
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss'],
standalone: true,
imports: [DatePipe],
})
export class AppComponent {
nowDateObject = Date.now(); // Date object
birthday = 972496541151; // Millisecond
}
Handling Timezones
Angular 17’s DatePipe allows for timezone specification:
<p>{{ today | date:'medium':'GMT+2' }}</p>This displays the date adjusted for the GMT+2 timezone.
5. Localization
To format dates according to different locales, use the locale parameter:
<p>{{ today | date:'long':'':'de-DE' }}</p>6. Best Practices
- Use ISO Strings for Consistency: When working with dates from APIs or databases, consider converting them to ISO strings for consistent handling: typescriptCopy
const isoDate = new Date().toISOString(); - Leverage Angular’s Internalization (i18n): For applications supporting multiple languages, use Angular’s i18n features in conjunction with
DatePipefor seamless localization. - Performance Considerations: While
DatePipeis efficient, for large lists of dates, consider formatting dates in the component class and using theasyncpipe for updates.
7. Performance Considerations
While DatePipe is efficient, for large lists of dates, consider formatting dates in the component class and using the async pipe for updates. This can help optimize performance, especially in scenarios involving frequent updates or long lists.
Conclusion: In summary, Angular 18’s DatePipe is a robust and versatile tool for handling date formatting within your applications. By familiarizing yourself with its numerous options and adhering to best practices, you can maintain consistent and localized date formats throughout your Angular projects.
It’s crucial to validate and sanitize date inputs, particularly those provided by users, to enhance the reliability of your applications. For more complex date manipulation tasks, you might want to integrate libraries such as date-fns or moment.js alongside Angular’s native features.
To stay informed about any updates or modifications to DatePipe in upcoming releases, regularly consult the latest Angular documentation.
Related Articles