We can control the UI in angular and handle user interaction such as input text and mouse event. We will be learning control input through two example
- Through component
- Handle user input through service
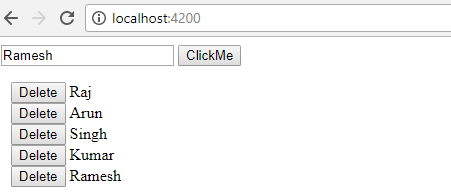
Case 1: In this example, we are handling input of angular through component. we are performing following task.
- Taking input type text called fname
- When clicking on a button that invokes a function called clickMe will display the text input on the screen.
- Clicking on the delete button will delete the item name from the list in angular.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div>
<input #fname>
<button (click) = "clickMe(fname.value)">ClickMe</button>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let user of users">
<button (click)="deleteMe(user)">Delete</button>
{{user}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>`,
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
users = ["Raj", "Arun", "Singh", "Kumar"];
clickMe(user){
console.log("new user = " +user);
this.users.push(user);
}
deleteMe(user){
console.log("delete user = " +user);
var index = this.users.indexOf(user);
if( index >= 0 ){
this.users.splice(index, 1);
}
}
}Notice the use of the #fname syntax as an identifier for an element, which in this case is an <input> element. Thus, The #fname syntax creates a reference to the <input> element that enables you to reference {{fname.value}} to see its value, or {{user.type}} to see the type of the input.
Case 2: Handling the user input through service in Angular.
In second example we will make two component <todo-input></todo-input><todo-list></todo-list> and one service file name called TodoService.ts
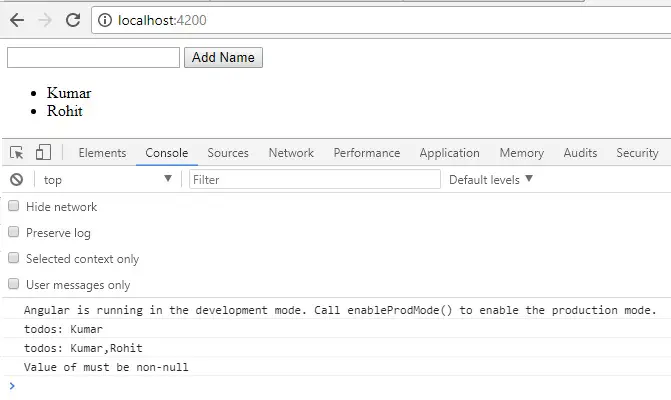
Add the following code in app.component.ts file
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `<div>
<todo-input></todo-input>
<todo-list></todo-list>
</div>`
})
export class AppComponent {
}Add the following code in app/todoinput.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { TodoService } from './todoservice';
@Component({
selector: 'todo-input',
template: `
<div>
<input type="text" #myInput>
<button (click)="mouseEvent(myInput.value)">Add Name</button>
</div>`
})
export class TodoInput {
constructor(public todoService: TodoService ){}
mouseEvent(value){
if((value != null) && (value.length > 0 )){
this.todoService.todos.push(value);
console.log("todos: " + this.todoService.todos);
} else {
console.log("Value of must be non-null");
}
}
}Add the following code in app/todolist.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { TodoService } from './todoservice';
@Component({
selector: 'todo-list',
template: `
<div>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let todo of todoService.todos">
{{todo}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>`
})
export class TodoList {
constructor(public todoService: TodoService ){}
mouseEvent(value){
if((value != null) && (value.length > 0 )){
this.todoService.todos.push(value);
console.log("todos: " + this.todoService.todos);
} else {
console.log("Value of must be non-null");
}
}
}We need to create service app/todoservice.ts, this file will contain a todos array that is updated with new to-do items when users click the <button> element in the root component.export class TodoService { todos= [];} At last, we need to register the component and service in app.module.ts file
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { TodoInput } from './todoinput';
import { TodoList } from './todolist';
import { TodoService } from './todoservice';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
TodoInput,
TodoList
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [ TodoService ],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }