Angular events binding is a crucial aspect of data binding in Angular. It allows developers to synchronize data between component properties and the view template, enabling interactive and responsive user interfaces. This article will explore event binding in Angular, covering its syntax, types, and practical examples.
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to use event binding, different types of events available in an Angular, and demonstrate a few examples of it. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What is Angular Event Binding?
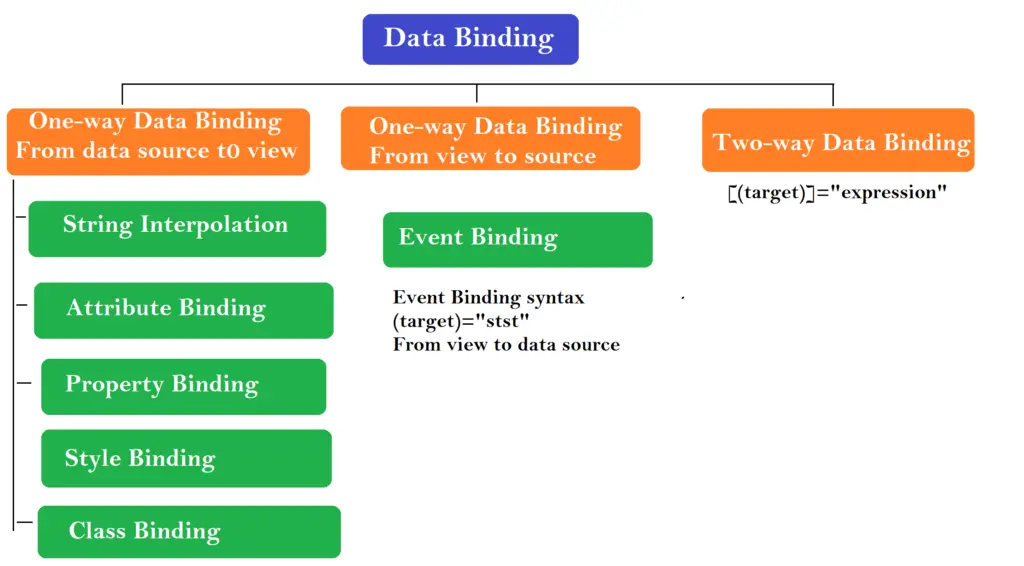
Angular event binding is a form of one-way data binding where data flows from the view template to the component class. It allows us to listen for and respond to user actions such as clicks, keystrokes, mouse movements, and more.
Angular Event Binding Syntax
The syntax for Angular event binding consists of the target event name within parentheses on the left and a quoted template statement on the right:
<element (eventName)="expression">
<element (eventName)="method()">
<element (eventName)="method($event)">Note: Remember, parentheses represent event binding and square brackets represent property binding.
For example:
<button (click)="onSubmit()">Submit</button>
In the above example, on the button tag, we add an event (click) to define what should happen when the button is clicked. When the (click) event happens we call we want to tell Angular to respond to the click event on the button, by invoking the update() method.
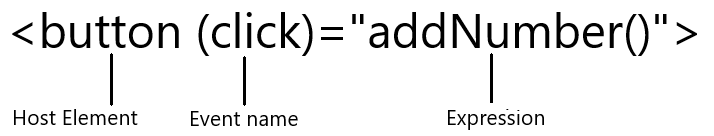
Angular event binding has the following parts:
- The host element is the source of events for the binding.
- The event name is what type of event to bind to the host element
- Expression is evaluated when the event is triggered, it can be an expression or method with and without parameters.
Angular Event binding simple example
In our first example of Event binding, we have a named variable containing ‘Keanu Reeves’ and it will display on the screen. We have a button, whenever we click on the Change name button it will invoke changeName() method and updates the value of the variable name to John Wick using a one-way event binding to the method the changeName(). The new updated name John Wick will render on screen.
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
<button (click)="changeName()">Change name</button>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
name: string = "Angular 17";
changeName() {
this.name = "Latest Angular";
}
}In this example, clicking the button changes the displayed name.
Types of Angular Event Listeners
Angular supports a wide range of event listeners. Here are some commonly used ones:
(click): Triggered when an element is clicked.(change): Fires when the value of an input element changes.(submit): Occurs when a form is submitted.(keyup),(keydown),(keypress): Keyboard events.(mouseenter),(mouseleave),(mousemove): Mouse events.(input): Fires when an input element receives user input.
Angular events example: Angular click event
We have got some idea about Angular event binding, let’s demonstrate a simple example of an Angular click event. Here is a screenshot of our first example of angular event binding.
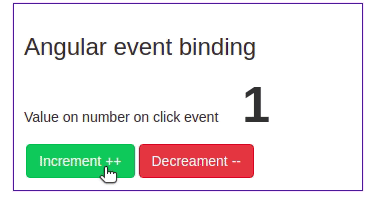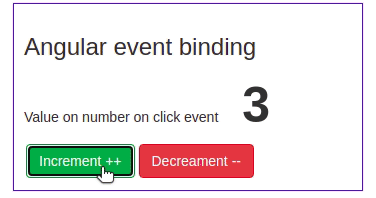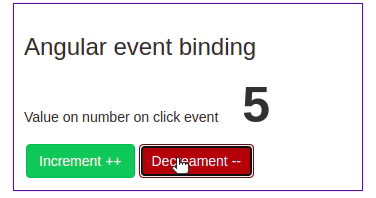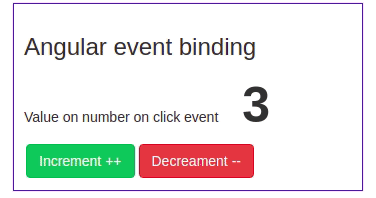
We have num variable property from component typescript file, and we have two-button with Angular click event. Clicking on increment will add a number by one and clicking on decrement will subtract a number by one. Let’s first define the num in the component typescript file.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
.....
export class AppComponent {
num = 1;
}Now in our component template, let’s add two buttons with Angular click event.
<section>
<h3>Angular event binding</h3>
<div>
Value on number on click event <span class="num-large">{{ num }}</span>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-success" (click)="num = num + 1">Increment ++</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger" (click)="num = num - 1">Decreament --</button></section>We used bootstrap for this UI, if you want to know the best approach for adding Bootstrap in Angular, then we have already covered a tutorial on it.
Types of Angular Event Listeners
Angular supports a wide range of event listeners. Here are some commonly used ones:
(click): Triggered when an element is clicked.(change): Fires when the value of an input element changes.(submit): Occurs when a form is submitted.(keyup),(keydown),(keypress): Keyboard events.(mouseenter),(mouseleave),(mousemove): Mouse events.(input): Fires when an input element receives user input.
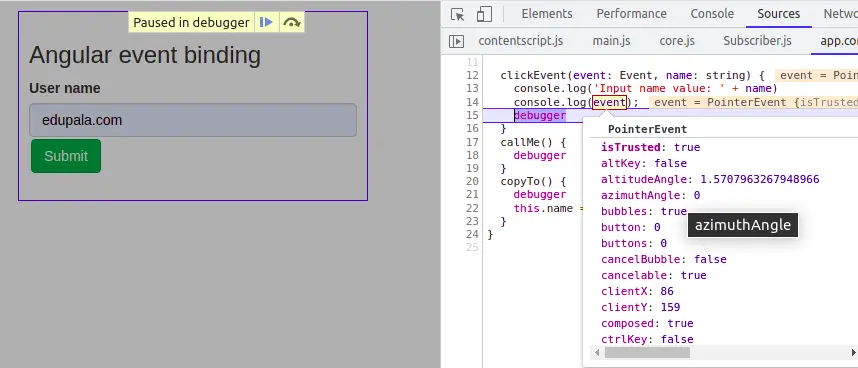
The $event Object
Angular provides the $event object, which contains detailed information about the triggered event. Here’s how to use it:
<input (keyup)="onKeyUp($event)">
typescript
onKeyUp(event: KeyboardEvent) {
console.log('Key pressed:', event.key);
}
Angular Mouse Events Example
Let’s create a component that changes its appearance based on mouse events:
@Component({
selector: 'app-mouse-events',
template: `
<div
(mouseover)="onMouseOver()"
(mouseout)="onMouseOut()"
[ngClass]="{'active': isActive}"
>
Hover over me!
</div>
`,
styles: [`
div {
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
transition: all 0.3s;
}
.active {
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
}
`]
})
export class MouseEventsComponent {
isActive = false;
onMouseOver() {
this.isActive = true;
}
onMouseOut() {
this.isActive = false;
}
}This example demonstrates how to use mouse events to create interactive UI elements.
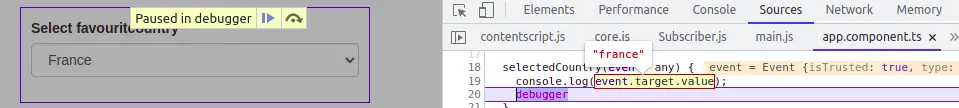
Select Element Change Event
In our last example, we’ll invoke the Angular change event on select input, here is a screenshot of the Angular change event.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-country-selector',
template: `
<div class="form-group">
<label for="countrySelect">Select favorite country</label>
<select id="countrySelect" (change)="selectedCountry($event)" class="form-control">
<option value="">--Please choose a country--</option>
<option value="india">India</option>
<option value="france">France</option>
<option value="germany">Germany</option>
<option value="canada">Canada</option>
</select>
</div>
<p *ngIf="selectedCountryName">You selected: {{ selectedCountryName }}</p>
`
})
export class CountrySelectorComponent {
selectedCountryName: string = '';
selectedCountry(event: Event) {
const selectElement = event.target as HTMLSelectElement;
this.selectedCountryName = selectElement.value;
console.log('Selected country:', this.selectedCountryName);
}
}Angular mouse events
In the Angular event list, we can see that there are many events available in Angular. Let’s demonstrate Angular mouse events on a div element. Whenever the mouse moves over the div, we call an event mouseOver, which in turn invokes a method over. In this method, we change the variable mouseOverDiv to true. On the mouseOut event, we call another method to change mouseOverDiv to false. Based on the value of mouseOverDiv, we change the div element’s background and font-weight value. Here is a screenshot of our example.
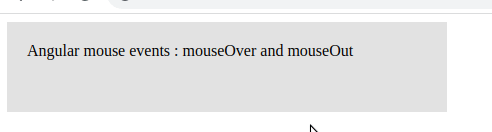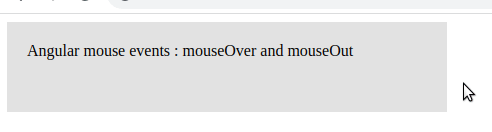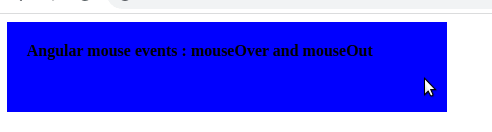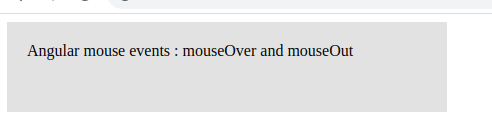
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-mouse-events',
template: `
<div class="container"
(mouseover)="onMouseOver()"
(mouseout)="onMouseOut()"
[ngClass]="{'div-in': isMouseOver, 'div-out': !isMouseOver}"
>
Angular mouse events: mouseover and mouseout
</div>
`,
styles: [`
.container {
padding: 20px;
height: 50px;
width: 400px;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
.div-in {
background: #3498db;
color: white;
font-weight: bold;
}
.div-out {
background: #e2e2e2;
color: black;
font-weight: normal;
}
`]
})
export class MouseEventsComponent {
isMouseOver: boolean = false;
onMouseOver() {
this.isMouseOver = true;
}
onMouseOut() {
this.isMouseOver = false;
}
}
Led add CSS style for our above example of Angular mouse events.
.container {
padding: 20px;
height: 50px;
width: 400px;
background: #e2e2e2
}
.div-in {
background: blue;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.div-out {
background-color:#e2e2e2;
font-weight: 400;
}Keyboard Events
Like mouse events, Angular also supports key events. In our previous example, we saw a click event. In a keyup event, whenever a keyboard key is pressed and released, we invoke an event handler to manage it. The keyup event is commonly used with input elements. Here is a screenshot of an Angular keyup event example.”
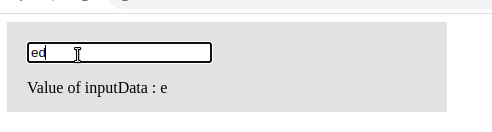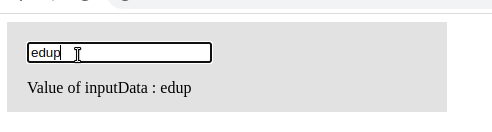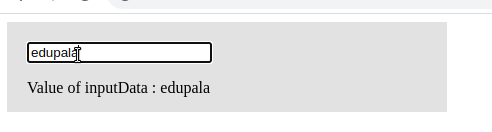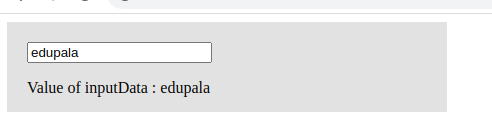
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-key-events',
template: `
<div class="container">
<input (keyup)="onKeyUp($event)" placeholder="Type something..." />
<p>You typed: {{ inputData }}</p>
<p>Key pressed: {{ lastKeyPressed }}</p>
</div>
`,
styles: [`
.container {
margin-top: 20px;
}
input {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
}
`]
})
export class KeyEventsComponent {
inputData: string = '';
lastKeyPressed: string = '';
onKeyUp(event: KeyboardEvent) {
const inputElement = event.target as HTMLInputElement;
this.inputData = inputElement.value;
this.lastKeyPressed = event.key;
console.log('Key pressed:', this.lastKeyPressed);
}
}These examples demonstrate how to handle various types of events in Angular, including form events, mouse events, and keyboard events. They showcase the use of event binding, property binding, and class binding, which are fundamental concepts in Angular’s template syntax.
Event binding is a powerful feature in Angular that allows developers to create interactive and responsive applications. By understanding and utilizing various event types, you can enhance user experience and build more dynamic web applications.
Conclusion:
Remember to always consider performance implications when using event binding, especially with frequently occurring events like mousemove or scroll. Use them judiciously and consider debouncing or throttling techniques for optimal performance.
As Angular continues to evolve, stay updated with the latest documentation for any new features or best practices related to event handling.
Related Post
- Angular two-way data binding – Angular ngModel
- Angular Data Binding in Angular
- Angular adds and removes classes using ngClass.
- Angular ngIf directive in details
- Angular ngSwitch directive in details
- How to implement an Angular search filter in Angular 13 | 14?
- How to calculate base64 image size in Angular
- How to install Angular material
- How to implement CKEditor in Angular
- How to use to implement HighCharts Angular